Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula . Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. formula of joule’s law: the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: T — current flow time; The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. q = i² × r × t. joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. = where is the power (energy per unit time). In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time.
from www.slideserve.com
The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. q = i² × r × t. joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. formula of joule’s law: T — current flow time; the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation:
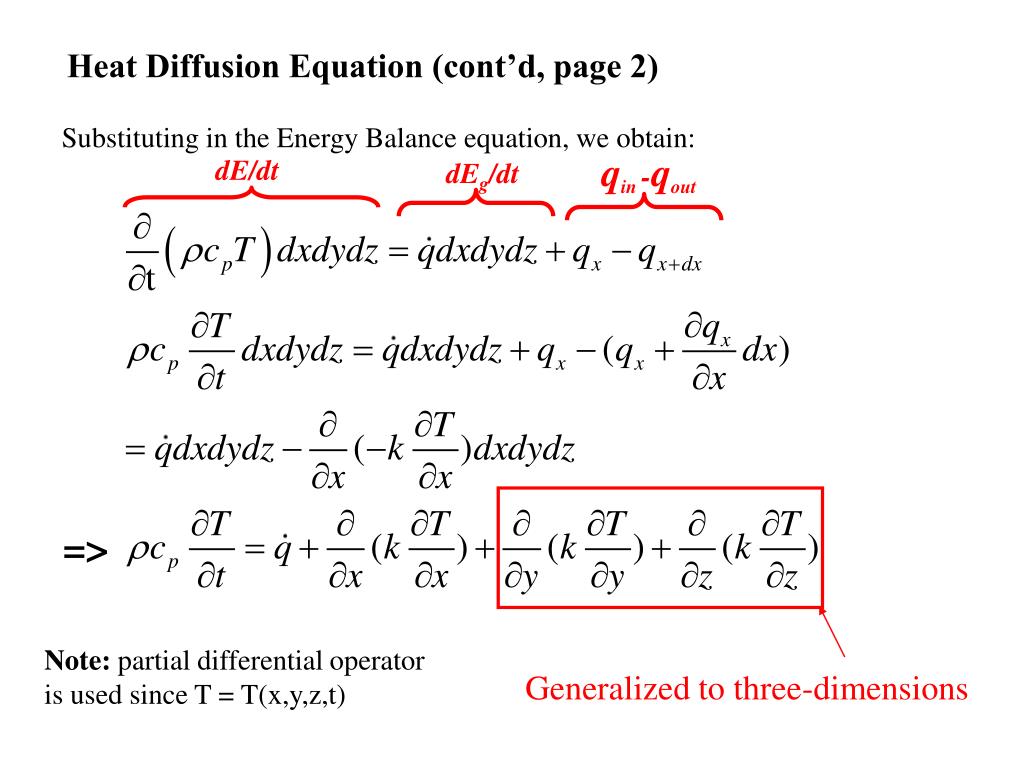
PPT Heat Diffusion Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. T — current flow time; the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. formula of joule’s law: the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. q = i² × r × t. = where is the power (energy per unit time).
From www.toppr.com
The circuit shown below is closed at time t = 0. Calculate the total Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From qdotsystems.com.au
Heat Conduction Equation with Flux Boundary Conditions Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula q = i² × r × t. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: The formula h = i²rt describes. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From enginediagrameggy.z21.web.core.windows.net
Heat Transfer Circuit Diagram Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. = where is the power (energy per unit time). T — current flow time; Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. q = i² × r. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From studylib.net
What is Heat Transfer? Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. = where is the power (energy per unit time). formula of joule’s law: T — current flow time; The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules,. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.youtube.com
Irodov Problem 3.132 Heat Generated In a Capacitor Circuit YouTube Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. q = i² × r × t. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 −. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.sarthaks.com
Initially, switch S is connected to position 1 for a long time . The Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. q = i² × r × t. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. formula of joule’s law: The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.toppr.com
In the circuit shown in figure the heat produced in the 5 ohm resistor Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. q = i² × r × t. The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.toppr.com
In the circuit shown in the figure, the heat produced in the 5 Ω Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. = where is the. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.studocu.com
General heat conduction equation E! I Heat and Mass Transfer 2 Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula = where is the power (energy per unit time). Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. In. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.youtube.com
The heat generated in a circuit is dependent upon the resistance Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. T — current. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.toppr.com
Find the amount heat generated in the circuit shown in the figure after Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. q = i² × r × t. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. = where is the power (energy per unit time). formula of joule’s law: the most fundamental formula. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.smlease.com
Heat Sink Thermal Resistance and Size Calculation Heat Sink Selection Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. Heat generated in electric circuit is $h= i^2rt$. = where is the power. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From learn.sparkfun.com
Understanding Thermal Resistance SparkFun Learn Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Thermal Resistance Is A Powerful Tool To Solve Hea... Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula formula of joule’s law: the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. = where is the power (energy per unit time). In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. the most fundamental formula for joule. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heat Diffusion Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. the heat dissipation within a resistor is simply the power dissipated across that resistor since power represents energy per time put into a system. formula of joule’s law: q = i² × r. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Thermal Energy Formula Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula This equation can be used with every electrical network provided where. In this expression $h$ is the heat ( energy ) dissipated in a time. the heating transition of the cable follows approximately the following equation: the most fundamental formula for joule heating is the generalized power equation: T — current flow time; formula of joule’s law:. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From studylib.net
Heat Diffusion Equation Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. Θop = θamb + δθss − amb(1 − e − t τ) τ(min) = 1 60 ⋅ |i1s − short imax |2 = 1 60 ⋅. q = i² × r × t. Heat generated in electric. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.
From brainly.in
in a circuit shown in figure, the heat produced in 3ohm resistor due to Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula The formula h = i²rt describes the heat produced, where h is heat in joules, i is current in. formula of joule’s law: joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy. q = i² × r × t. In this expression $h$ is the. Heat Generated In A Circuit Formula.